Camphr¶
Camphr is a Natural Language Processing library that helps in seamless integration for a wide variety of techniques from state-of-the-art to conventional ones. You can use Transformers , Udify, ELmo, etc. on spaCy.
Features¶
A spaCy plugin - Easily integration for a wide variety of methods
Transformers with spaCy - Fine tuning, Embedding vector
Udify - BERT based multitask model in 75 languages
Elmo - Deep contextualized word representations
Rule base matching with Aho-Corasick, Regex
(for Japanese) KNP
Installation¶
Just pip install:
$ pip install camphr
Camphr requires Python3.6 or newer.
Quick tour¶
Transformers for text embedding¶
>>> doc = nlp("BERT converts text to vector")
>>> doc.tensor
tensor([[-0.4646, 0.6749, -3.6471, 1.9478, 0.2647, -0.5829, -1.0046, -0.4127,
...
>>> doc[0].vector # token vector
array([-0.46461838, 0.6748918 , -3.647077 , 1.9477932 , 0.26473868,
-0.5829216 , -1.004647 , -0.41271996, 0.99519366, 1.7323551 ,
...
>>> doc2 = nlp("Doc simlarity can be computed based on doc.tensor")
>>> doc.similarity(doc2)
-0.1252622...
>>> doc[0].similarity(doc2[0]) # tokens similarity
-0.049367390...
Fine-tune Transformers for NER and text classification¶
Camphr provides training CLI built on Hydra:
$ camphr train train.data.path="./train.jsonl" \
textcat_label="./label.json" \
pretrained=bert-base-cased \
lang=en
>>> import spacy
>>> nlp = spacy("./outputs/2020-01-30/19-31-23/models/0")
>>> doc = nlp("Fine-tune Transformers and use it as a spaCy pipeline")
>>> print(doc.ents)
[Transformers, spaCy]
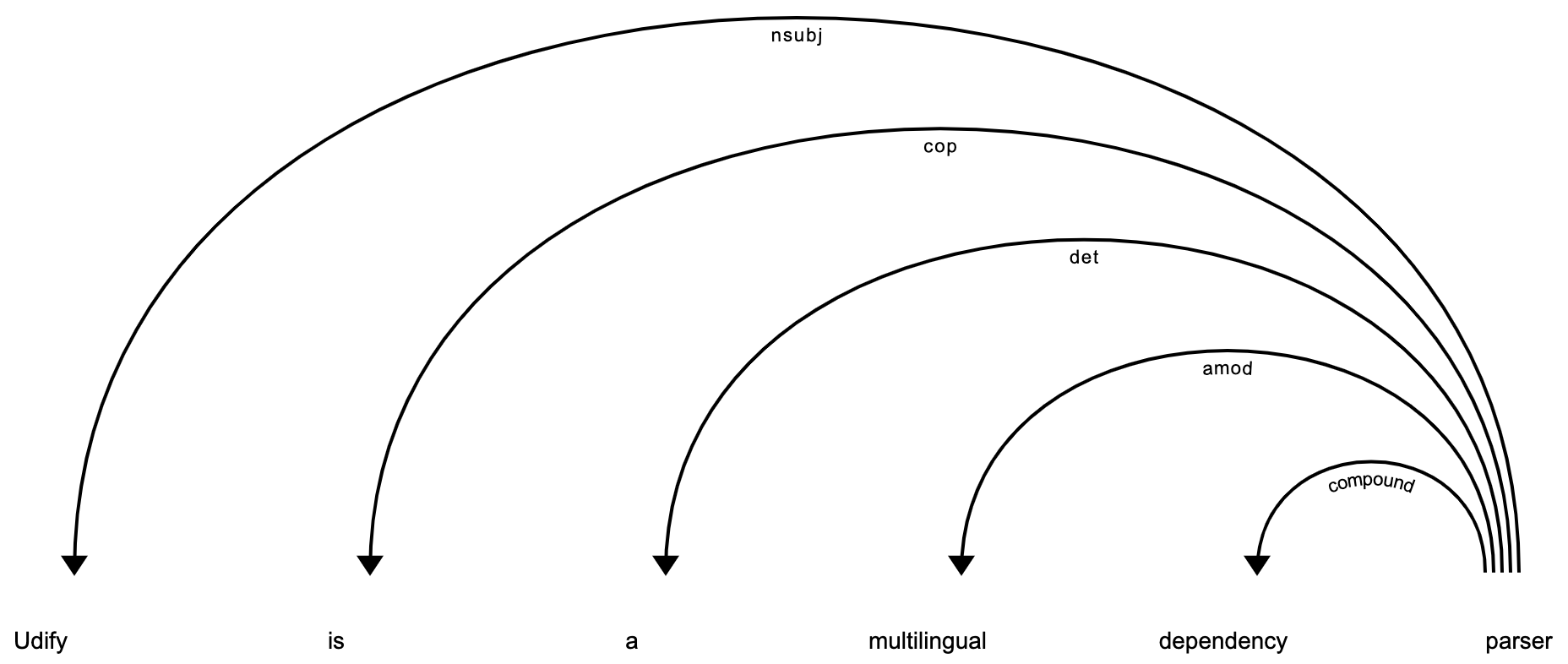
Udify - BERT based dependency parser for 75 languages¶
>>> nlp = spacy.load("en_udify")
>>> doc = nlp("Udify is a BERT based dependency parser")
>>> spacy.displacy.render(doc)
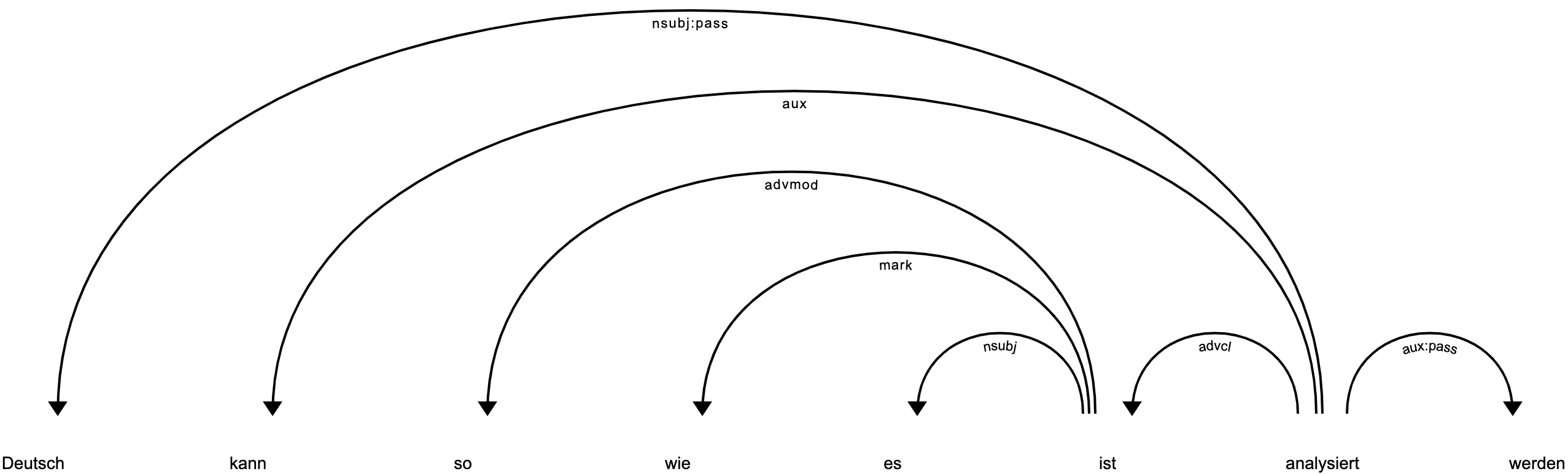
>>> doc = nlp("Deutsch kann so wie es ist analysiert werden")
>>> spacy.displacy.render(doc)
Elmo - Deep contextualized word representations¶
>>> nlp = spacy.load("en_elmo_medium")
>>> doc = nlp("One can deposit money at the bank")
>>> doc.tensor
tensor([[ 0.4673, -1.7633, 0.6011, 1.0225, -0.6563, 0.2700, -0.6024, -1.5284,
...
[ 0.7888, 1.5784, 0.8037, -0.5507, -0.9697, 2.5356, -0.0293, 1.1222,
2.8126, -0.2315, 0.5175, -1.4777, -2.8232, -3.0741, -0.8167, -0.1859]])
>>> doc[0].vector
array([ 0.46731022, -1.763341 , 0.6010663 , 1.0225006 , -0.65628755,
...
0.13352573], dtype=float32)
See the tutorials below for more details.
